Introduction
Kyphosis, often described as an abnormal curvature of the spine resulting in a rounded back, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. As a spine surgeon at Bangalore Spine Specialist Clinic, Dr. Shashidhar B K emphasizes the importance of understanding this condition, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
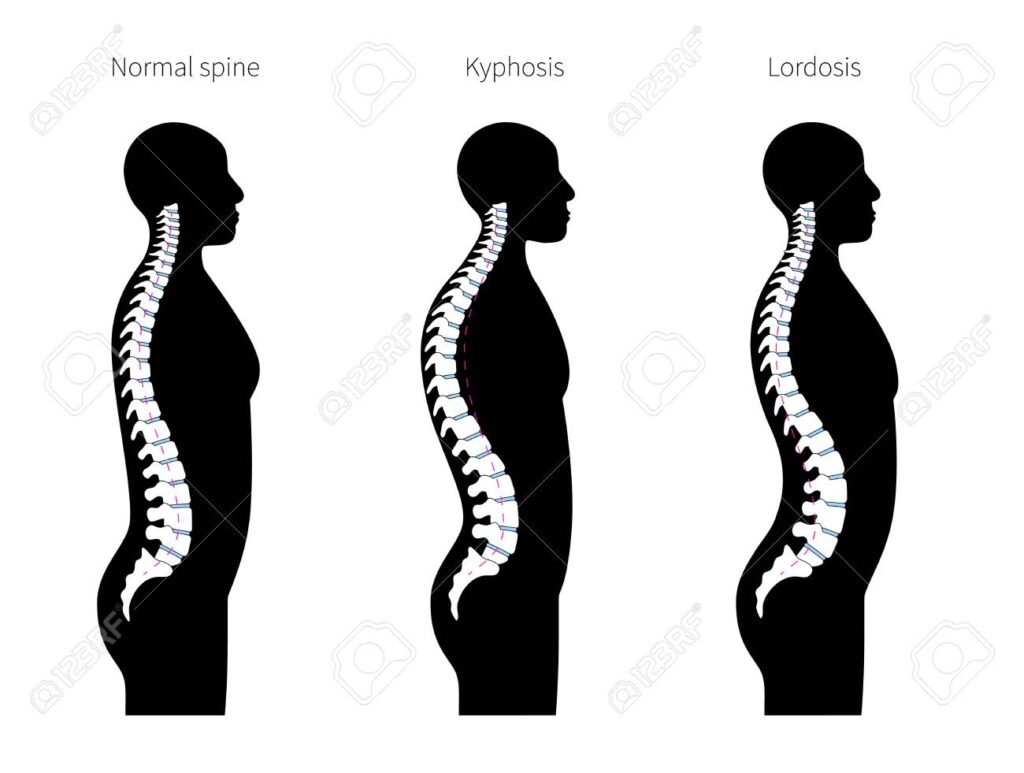
What is Kyphosis?
Kyphosis is characterized by an excessive outward curvature of the thoracic spine, leading to a hunchback appearance. While some degree of kyphosis is normal, excessive curvature can lead to discomfort, pain, and mobility issues. The condition can develop at any age, but it is particularly prevalent in adolescents and older adults.
Types of Kyphosis
- Postural Kyphosis: Often seen in adolescents due to slouching or poor posture.
- Scheuermann’s Kyphosis: A more severe form that occurs during growth spurts, typically in adolescents.
- Congenital Kyphosis: A rare condition present at birth due to malformation of the spine.
- Degenerative Kyphosis: Often seen in older adults due to degenerative disc disease and osteoporosis.
Causes of Kyphosis
Kyphosis can arise from various factors, including:
- Genetic Factors: Congenital defects can lead to structural abnormalities in the spine.
- Trauma: Injuries to the spine can result in deformities.
- Degenerative Diseases: Conditions like arthritis and osteoporosis can weaken spinal structures.
- Infections: Spinal infections can lead to deformities.
- Neuromuscular Conditions: Conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy can contribute to kyphosis.
Symptoms of Kyphosis
Patients with kyphosis may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Visible Hunchback: A noticeable curvature of the spine.
- Back Pain: Discomfort or pain in the back, particularly after prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
- Fatigue: Increased fatigue due to muscle strain.
- Breathing Difficulties: Severe cases may affect lung capacity and breathing.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing kyphosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A thorough assessment of posture and spinal curvature.
- Medical History: Understanding the patient’s symptoms and any relevant medical history.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be used to assess the degree of curvature and identify underlying issues.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help improve posture and alleviate pain.
- Bracing: In adolescents with Scheuermann’s kyphosis, braces may be effective in preventing progression.
- Pain Management: Medications such as NSAIDs can help manage discomfort.
Surgical Treatments
For severe cases of kyphosis, especially those causing significant pain or functional impairment, surgical intervention may be necessary. Dr. Shashidhar B K specializes in various surgical techniques, including:
- Spinal Fusion: Connecting two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine.
- Osteotomy: Reshaping the spine to correct deformities.
- Vertebral Column Resection: Removing a portion of the vertebra to correct severe deformities.
Preventive Measures
While not all cases of kyphosis can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce the risk:
- Maintain Good Posture: Encouraging proper posture during activities can help prevent postural kyphosis.
- Strengthening Exercises: Regular exercises focusing on core and back strength can support spinal health.
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection through regular spinal assessments can help manage kyphosis effectively.
Conclusion
Understanding kyphosis is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. With advancements in treatment options and a focus on patient-centered care, individuals suffering from kyphosis can achieve significant improvements in their quality of life. At Bangalore Spine Specialist Clinic, Dr. Shashidhar B K is dedicated to providing comprehensive care for patients with spinal disorders, ensuring they receive the best possible treatment tailored to their needs.
